Couplings
Coupling
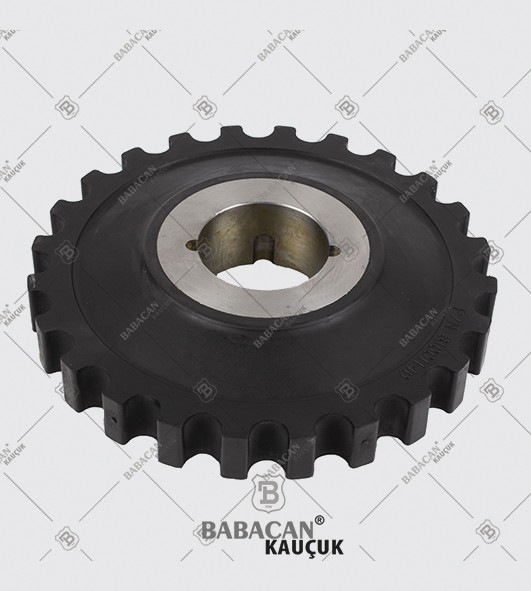
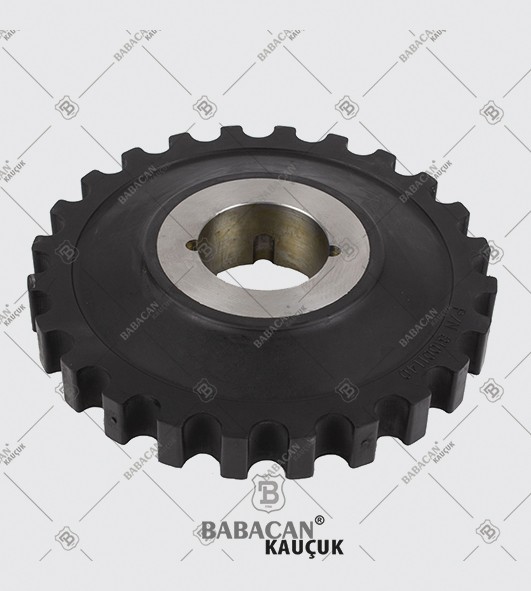
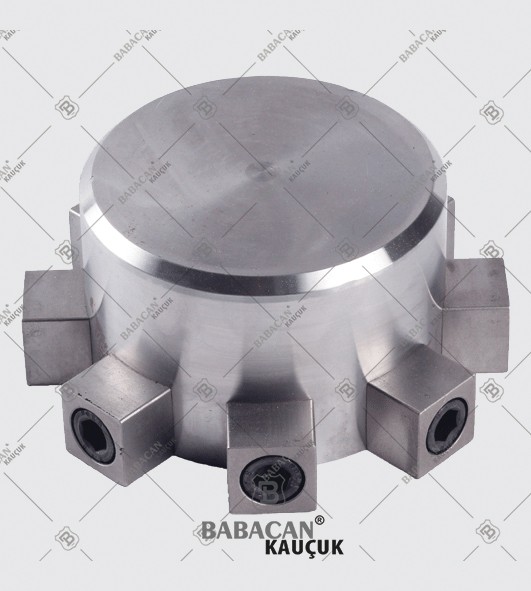
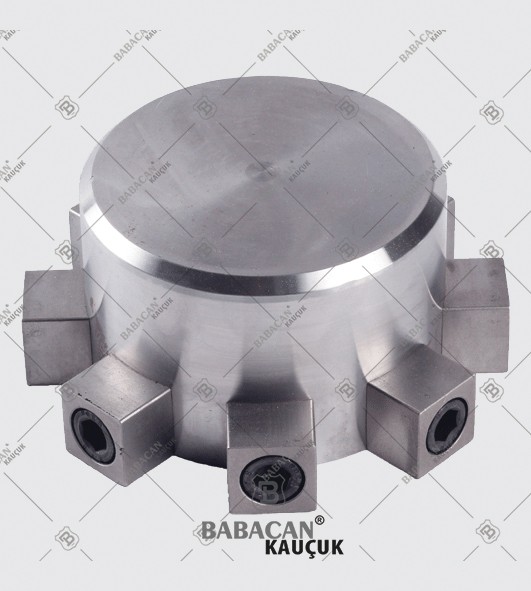
Our range of Coupling meets the highest standards of quality which provides them superior performance for a longer period of time. Available in flexible designs and superior quality our Rubber Coupling are offered as per the requirements of our clients at industry leading prices.
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. Couplings do not normally allow disconnection of shafts during operation, however there are torque limiting couplings which can slip or disconnect when some torque limit is exceeded.
The primary purpose of couplings is to join two pieces of rotating equipment while permitting some degree of misalignment or end movement or both. By careful selection, installation and maintenance of couplings, substantial savings can be made in reduced maintenance costs and downtime.
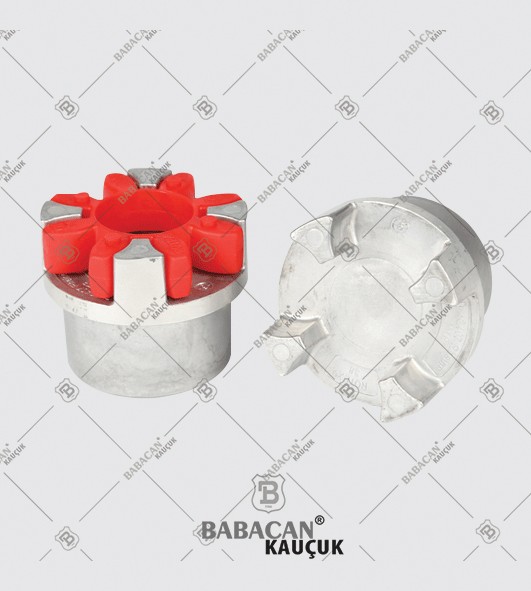
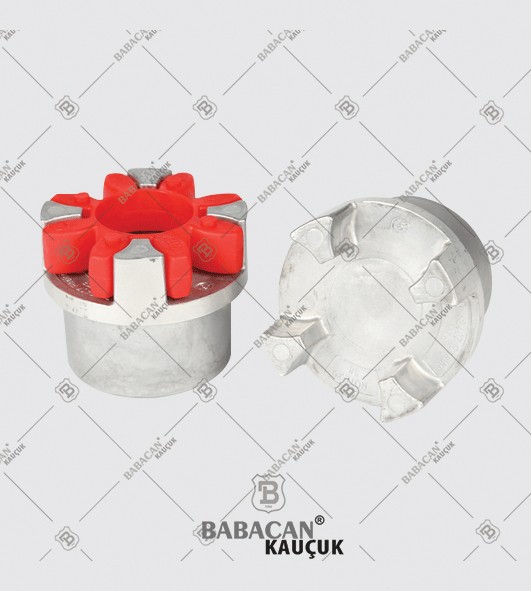
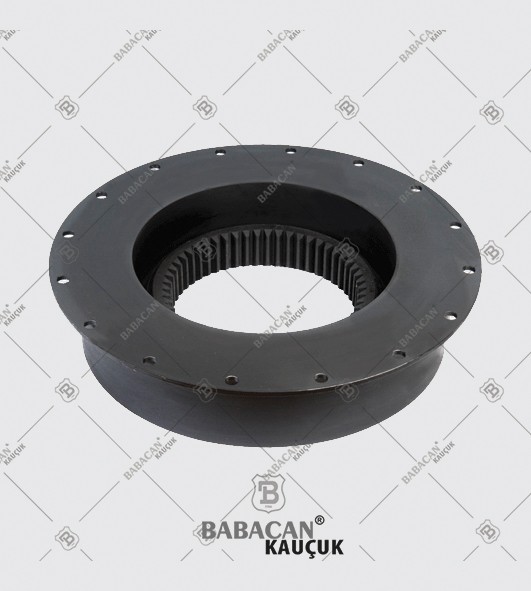
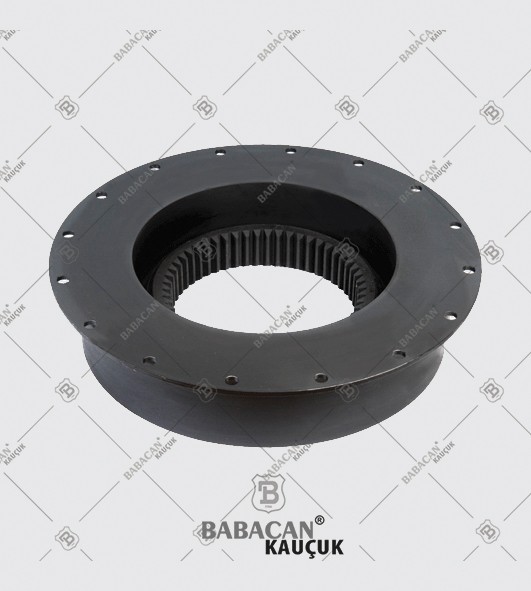
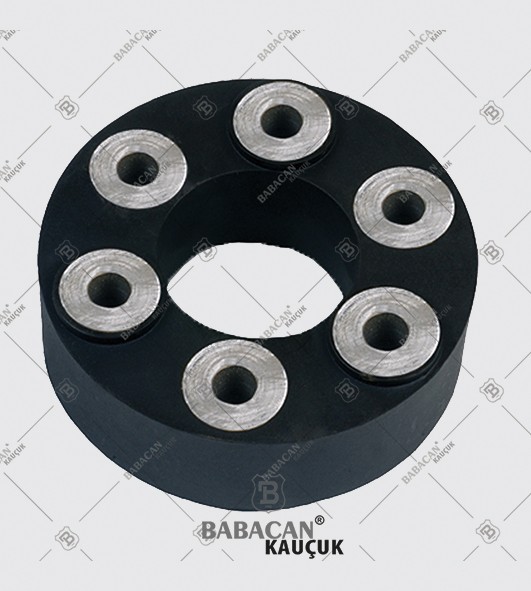
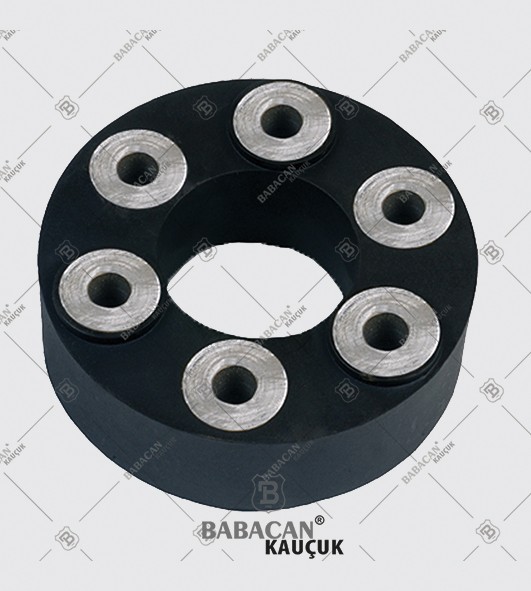
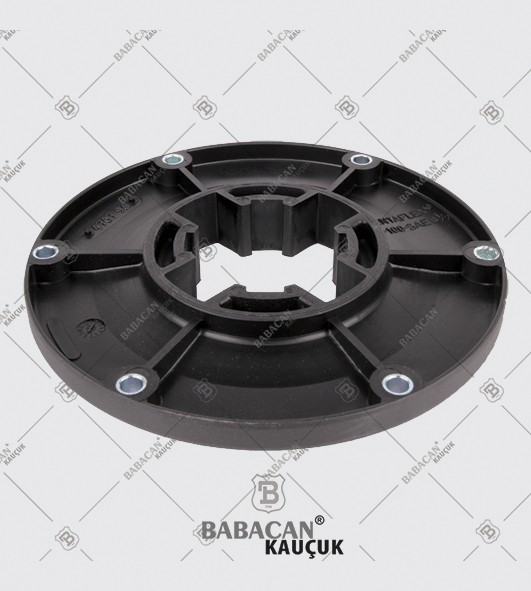
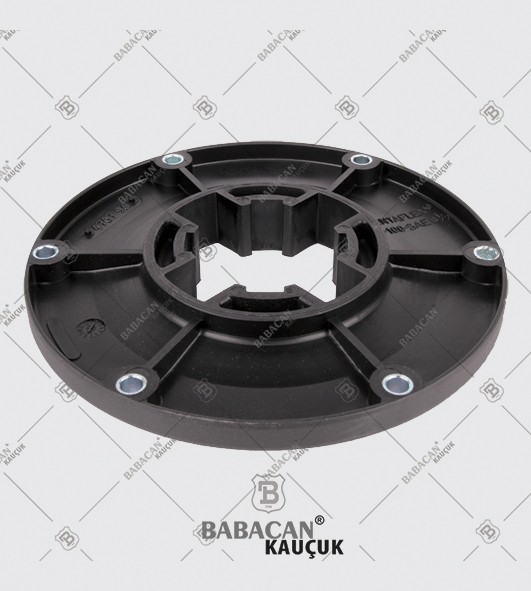
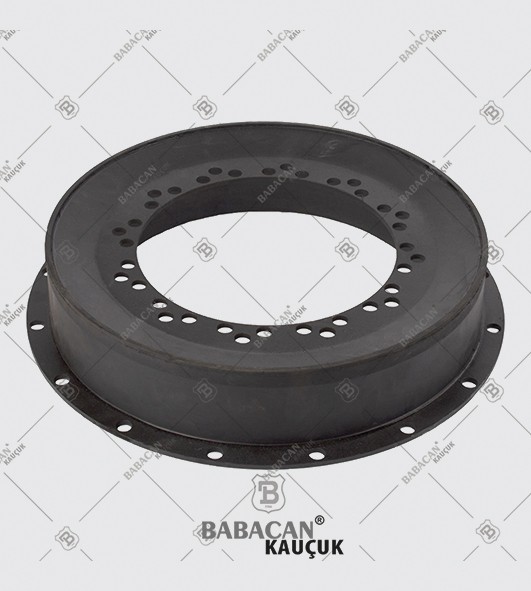
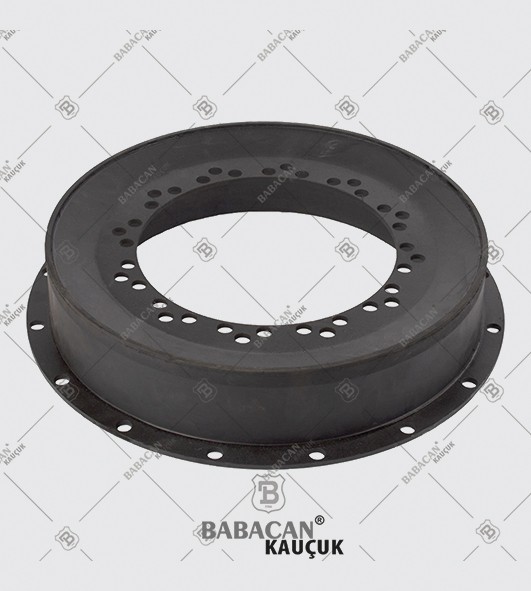
The Rubber disc coupling permits a quick and simple connection to be made between a flange - especially a flywheel - and a shaft. A modified design can also be used to connect two shafts. The realized connections are free from backlash.
The Rubber disc coupling is an axial coupling where both the complete coupling and the flexible element can be easily fitted and dismantled.
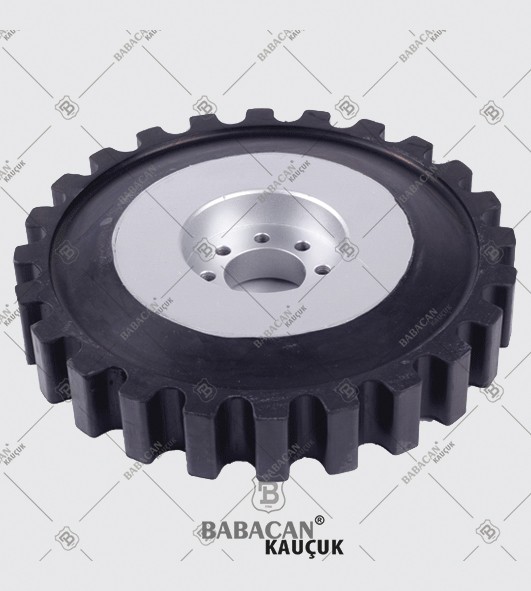
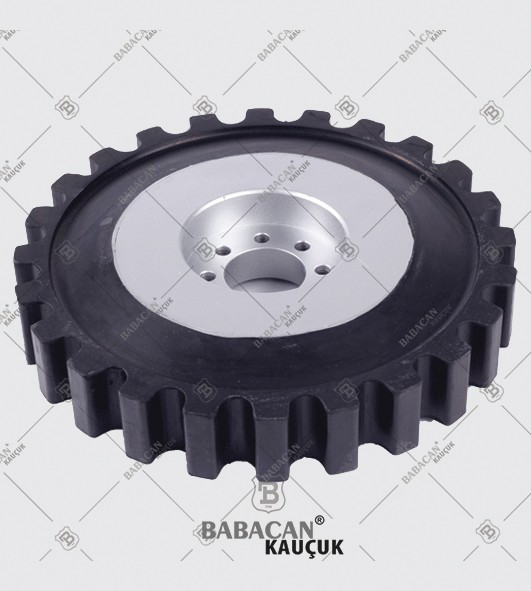
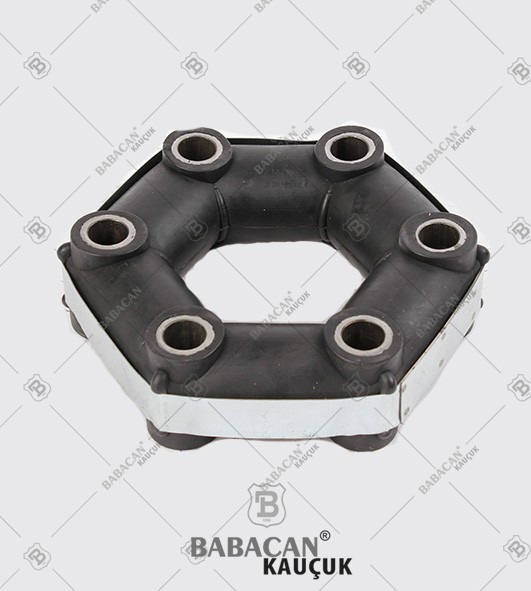
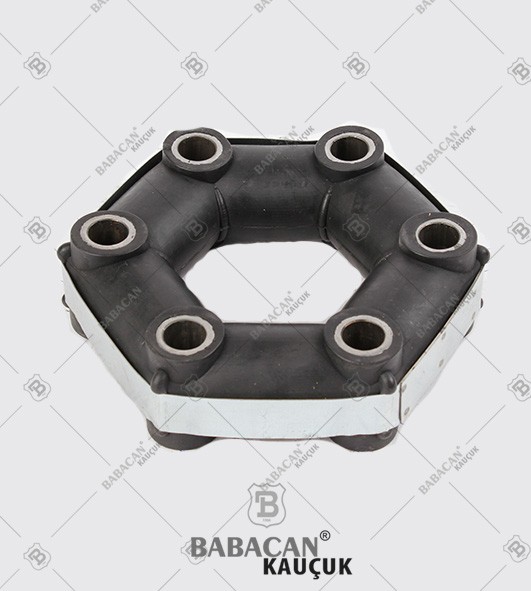
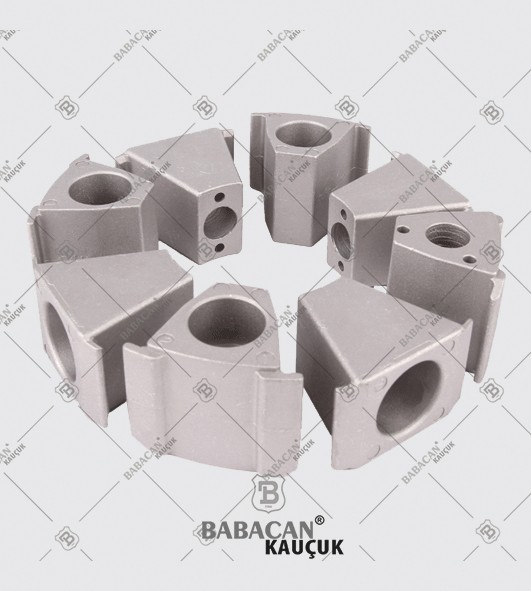
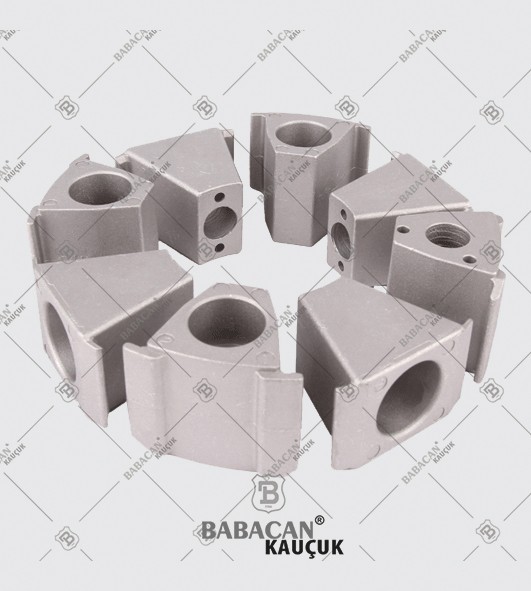
Flexible couplings are used to transmit torque from one shaft to another when the two shafts are slightly misaligned. Flexible couplings can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment up to 3° and some parallel misalignment. In addition, they can also be used for vibration damping or noise reduction.
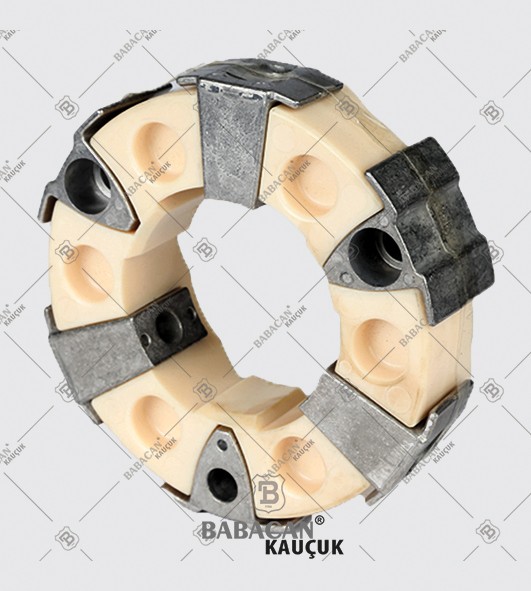
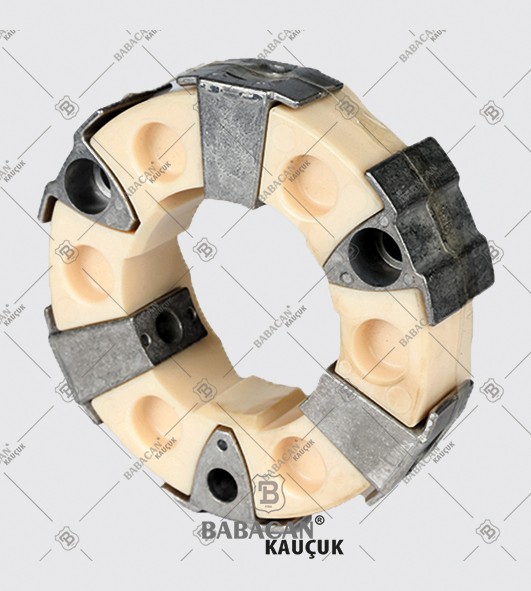
Disc couplings transmit torque from a driving to a driven bolt tangentially on a common bolt circle. Torque is transmitted between the bolts through a series of thin, stainless steel discs assembled in a pack. Misalignment is accomplished by deforming of the material between the bolts
Coupling
Our range of Coupling meets the highest standards of quality which provides them superior performance for a longer period of time. Available in flexible designs and superior quality our Rubber Coupling are offered as per the requirements of our clients at industry leading prices.
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. Couplings do not normally allow disconnection of shafts during operation, however there are torque limiting couplings which can slip or disconnect when some torque limit is exceeded.
The primary purpose of couplings is to join two pieces of rotating equipment while permitting some degree of misalignment or end movement or both. By careful selection, installation and maintenance of couplings, substantial savings can be made in reduced maintenance costs and downtime.
The Rubber disc coupling permits a quick and simple connection to be made between a flange - especially a flywheel - and a shaft. A modified design can also be used to connect two shafts. The realized connections are free from backlash.
The Rubber disc coupling is an axial coupling where both the complete coupling and the flexible element can be easily fitted and dismantled.
Flexible couplings are used to transmit torque from one shaft to another when the two shafts are slightly misaligned. Flexible couplings can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment up to 3° and some parallel misalignment. In addition, they can also be used for vibration damping or noise reduction.
Disc couplings transmit torque from a driving to a driven bolt tangentially on a common bolt circle. Torque is transmitted between the bolts through a series of thin, stainless steel discs assembled in a pack. Misalignment is accomplished by deforming of the material between the bolts.